With the start of a new year comes a favorite tradition at Wheaton Archives & Special Collections – taking a moment to look back at some of the fascinating “new” old materials that found their way to the Archives over the last year. Below is a review of selected highlights from the Archives’ 2025 acquisitions:
Evangelism & Missions Archives
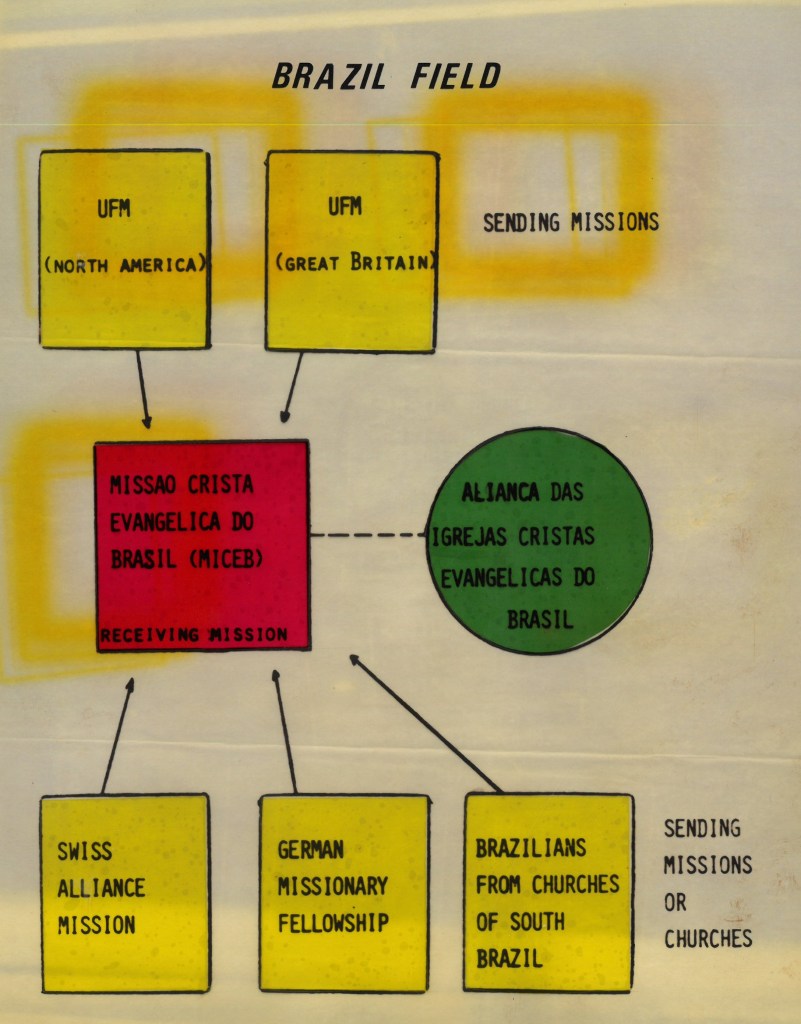
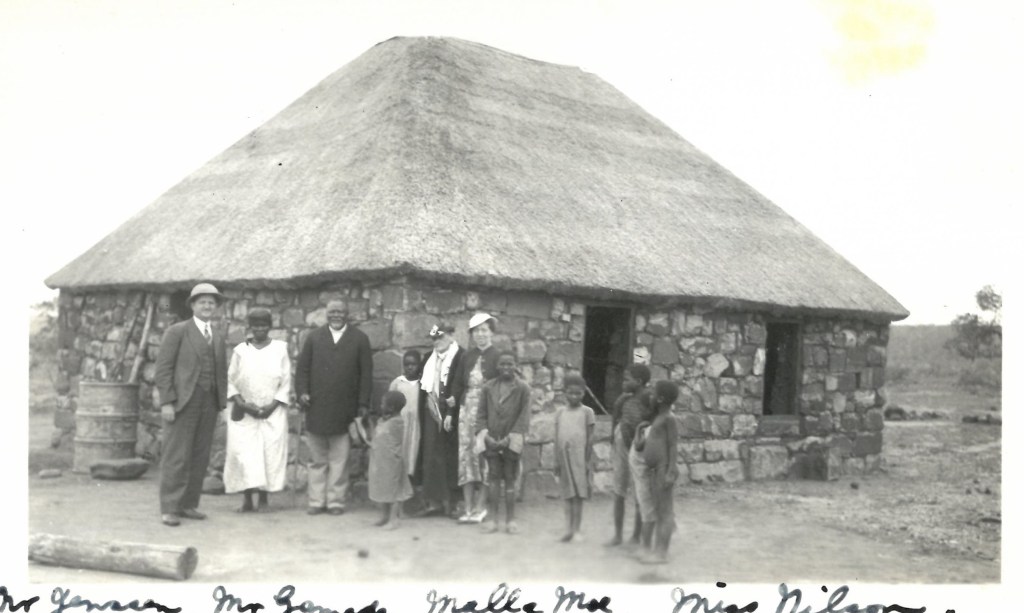
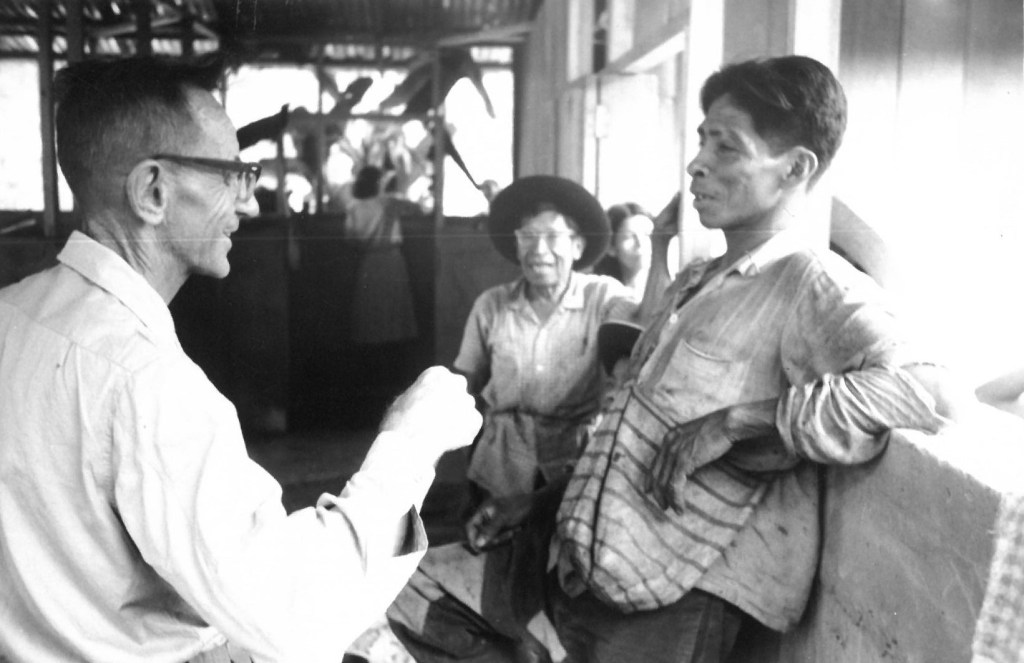
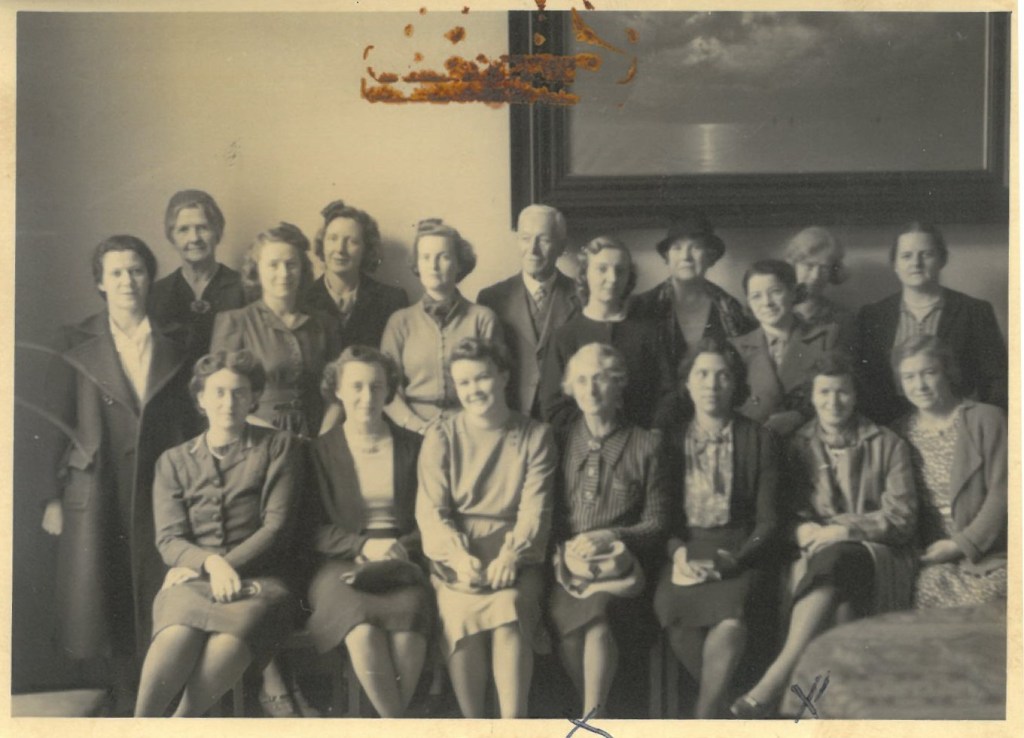
Perhaps the most significant additions to the Evangelism & Missions Archives were the large accessions we received from evangelical foreign mission associations. SEND International (formerly Far Eastern Gospel Crusade), Crossworld (formerly Unevangelized Field Mission), The Evangelical Alliance Mission (TEAM), and SIM International are each multimillion dollar organizations that between them have thousands of workers on five continents. SIM, in particular, was born out of the merger of several different missions active in North and South America, Africa, Asia and Europe. Together these mission organizations gave more than 100 linear feet of their files to the Archives (TEAM has been donating materials since 2022) with other large accessions from SIM expected in 2026. In addition, the family of John Gration, a missionary of Africa Inland Mission and long-time professor of missions at Wheaton College, gave his files on the history of AIM, including the manuscript of his dissertation. Together these different accessions give an extraordinarily detailed pictures of North American Protestant missions around the world in the 20th and 21st centuries.
Continue reading






